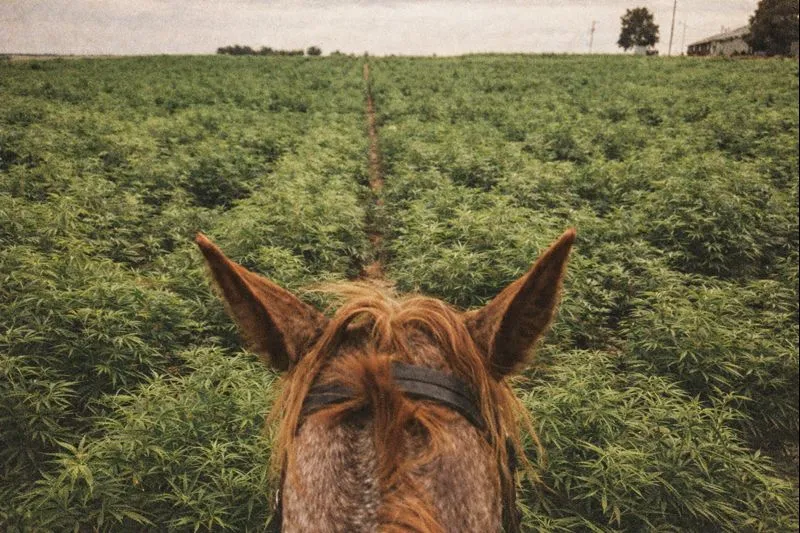
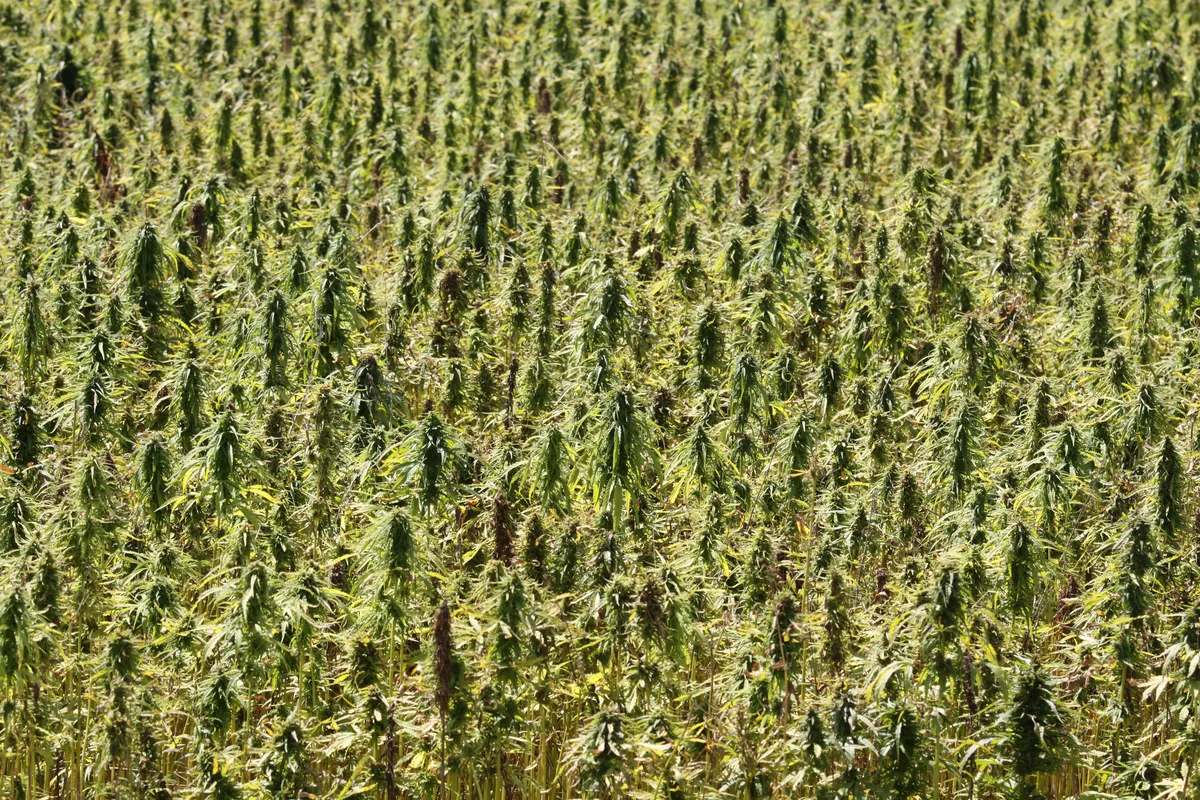
Offsetting: Hemp Carbon storage, more than one hectare of forest
Hemp can absorb more C02 than other plants: the biomass-so can be used for green building, bioplastics, biochar, for a longer storage
Hemp, photosynthesis, carbon storage capacity
Hemp is considered a hardy species in that it is able to grow under suboptimal conditions in terms of both soil fertility and temperature and water availability. It is a plant that can store carbon dioxide at higher temperatures (up to 30-35 °C) and thus perform photosynthesis and continue the phenological process unhindered even under more extreme conditions.
One hectare of hemp can absorb eight to twenty-two tons of CO2 per year, while a hectare of tree plants averages around six tons as reported by Hudson Carbon in New York.
Focusing on the carbon storage capacity of hemp is possible when it comes to green building use. This CO2 is sequestered in the stem, which accounts for 80 percent of crop biomass-so using its products to make durable materials (green building, bioplastics, biochar) allows CO2 absorbed from the atmosphere to be sequestered for a period of time.
This explanation – with further considerations – allows us to understand the sentence that claims how one hectare of hemp can absorb more CO2 than one hectare of forest.
What is Carbon offset?
Carbon offsetting is defined as any activity aimed at offsetting the emission of carbon dioxide. It may represent in the future an opportunity for a reed farmer to increase his or her income.
The introduction of a carbon credits market will make it possible to quantify and reward the contribution. One carbon credit is equivalent to one ton of carbon dioxide stored.
Carbon Farming
Carbon Farming refers to an agro-ecosystem that can harness the natural ability of soil and plants to store carbon by removing it from the atmosphere.
Contributing to the European Green Deal to mitigate and innovate against climate change is a concept to be encouraged especially in the agriculture and forestry sector. From December 2021, the commission through the “Communication on sustainable carbon cycles” has given the green light for European agriculture to enter the carbon credit market through the practice of carbon farming.
The goal is to save about 42 million tons of CO2 in the EU by 2030. Carbon farming or agro-ecology has great potential to generate positive ecological, economic and social impacts.
As per today, hemp is just a potential asset.