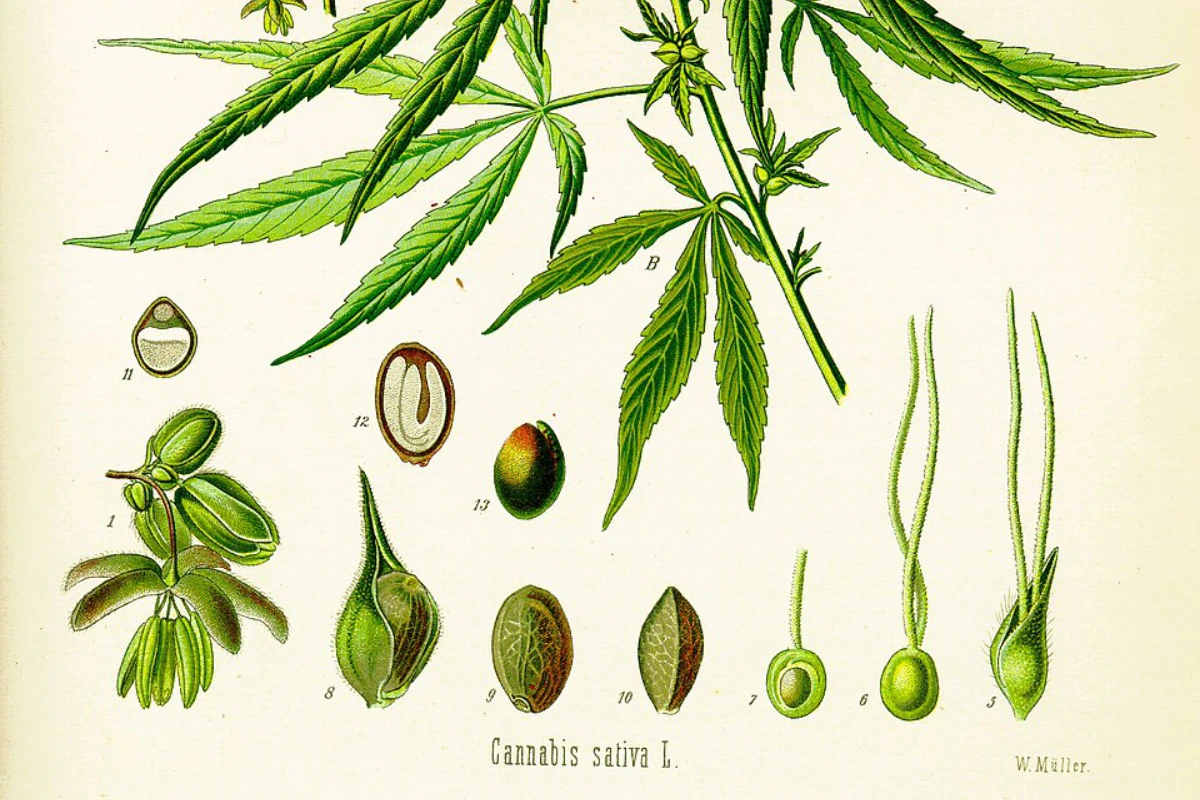
Hemp: the difference between CBD and THC
Which is the difference between CBD and THC? CBD presents anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antioxidant activity – THC produces psychotropic effects
Hemp: what is CBD? On hemp’s CBD: the topic is still confused
CBD (cannabidiol), a phytocannabinoid among the most studied by science for its beneficial properties on the human body. Analyses highlight inflammatory effects.
The differences between CBD and THC in hemp
The differences between CBD with THC is the cell receptor with which they interact. CBD targets the CB2 receptor, which is present in almost every cell and organ in the human body. THC goes on to bind directly to the CB1 receptor, in the central nervous system. Only THC produces psychotropic effects that have established the legal ban as a soft drug.
The properties of CBD extracted from hemp: anxiolytic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic
According to part of the scientific community, CBD is a useful analgesic. Thus, among the beneficial effects of CBD is the ability to reduce forms of anxiety such as post-traumatic stress disorder and obsessive compulsive disorder. It then helps combat insomnia and depression. Anti-inflammatory action is also highlighted, which is useful in treatments of skin conditions (such as psoriasis). The antioxidants present in CBD are then used in both cosmetics.
Side effects of CBD
Beyond the growing market interest in CBD and the increasing number of studies highlighting beneficial properties, it is mandatory to mention that, to date, there is no fully shared and formal protocol that can give guidance when assuming CBD, such as concentration rates and storage methods.
Although it is generally recognized as a safe product, pending further confirmation, there are those who warn of possible side effects, on par with any drug or medication. Dry mouth, lightheadedness, drowsiness and nausea are cited, especially if too high a dose of CBD has been taken.
Legislation: is CBD legal?
Yes, CBD is legal. In Italy, the rule is that the production and sale of cannabidiol products is allowed if the present concentration of THC, which is not easy to separate entirely from other chemical compounds, is less than or equal to 0.6 percent (originally it was 0.2 percent).